Jira is often associated with software development, agile teams, and bug tracking. It’s a tool many developers can’t live without. But, can it be used for task management outside of the tech world? The short answer is yes. Jira’s flexibility allows it to handle a wide range of tasks, even for teams in marketing, HR, operations, or any department that needs to manage workflows and deadlines efficiently.
This article explores how Jira can be used for task management in various industries and teams, its advantages, disadvantages, and a comparison with other task management tools like Trello, Asana, and Monday.com. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how Jira works as a task management tool and whether it suits your team’s needs.
What is Jira?
Jira, developed by Atlassian, began as a bug and issue-tracking tool for software developers. However, its robust framework and customizable features quickly made it popular for agile project management, particularly in teams using Scrum and Kanban methodologies. Over time, Jira evolved to be more than just a tool for developers; it became a versatile platform that can be adapted to fit different industries and workflows.
But is it strictly limited to development teams? Absolutely not. Many non-tech teams have successfully adopted Jira for general task management, managing everything from marketing campaigns to HR operations. Its strength lies in its flexibility. Jira allows you to customize your project boards, task types, and workflows, enabling you to tailor it for different business needs.
Jira as a Task Management Tool
Jira’s versatility extends beyond traditional project management. It is highly effective for day-to-day task management, especially for teams looking to track tasks, assign responsibilities, and ensure work gets done on time. Here’s how Jira functions as a task management tool:
1. Task Creation and Assignment
In Jira, tasks are referred to as “issues.” You can create different types of issues based on your workflow, such as tasks, bugs, stories, or sub-tasks. This flexibility makes it easy to assign tasks to different team members, track their progress, and add details like deadlines, comments, and attachments.
Once a task is created, it can be assigned to a specific person, team, or department. The assignee is notified about the task, ensuring that everyone is aligned on their responsibilities. Tasks can also be tagged, labeled, and categorized to make searching easier.
2. Customizable Workflows
One of Jira’s biggest advantages is its customizable workflows. In the context of task management, you can set up workflows that fit your team’s unique process. For instance, a typical task management workflow might include statuses like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.”
However, if your team requires a more complex process, you can add stages like “Awaiting Approval,” “QA Testing,” or “Blocked” to ensure every part of the process is accounted for. This ability to create custom workflows means Jira can adapt to both simple and complex task management needs.
3. Visual Task Boards
Jira’s task boards—either Kanban or Scrum boards—give a visual overview of your team’s tasks and their current status. Each task is represented by a card that can be moved from one stage to another, making it easy to track progress. This visual representation helps teams understand what’s in progress, what’s coming up, and what’s been completed.
For task management, many teams prefer Kanban boards, which allow for continuous workflow management. You can create columns representing stages in the workflow (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done) and drag tasks between them as they progress. This simple, visual approach helps teams stay organized and ensures nothing falls through the cracks.
4. Tracking Deadlines and Progress
In task management, tracking deadlines is essential to ensure work is completed on time. Jira allows you to set due dates for tasks, assign priority levels, and track how long a task has been in progress. The system also offers notifications and reminders, so users don’t miss important deadlines.
Jira’s reporting capabilities provide insights into your team’s progress, helping you understand where tasks are getting stuck and which tasks are at risk of missing their deadlines. These reports can help team leaders identify bottlenecks and improve overall productivity.
5. Real-Time Collaboration
Jira promotes collaboration by allowing team members to comment on tasks, upload files, and tag colleagues directly within the task card. This ensures that all communications related to a task are centralized, reducing the need for endless email threads or multiple tools for task discussions.
By having everything in one place, teams can easily keep track of task updates, changes in priorities, or feedback from stakeholders. This level of collaboration is particularly beneficial for remote or distributed teams that need a central platform to manage their workflows.
Setting Up Jira for Task Management: A Step-by-Step Guide
Jira can be intimidating for new users, especially those unfamiliar with project management tools. However, setting up Jira for task management can be simplified with a few basic steps. Here’s how to set up Jira for managing tasks efficiently:
1. Create a New Project
The first step is to create a new project in Jira. When doing this, you’ll need to select the project template that fits your needs. For task management, the Kanban or Scrum project templates are ideal. While Scrum is great for teams working in short cycles (sprints), Kanban is better suited for continuous task management.
Once you’ve selected your template, you can name your project and define its purpose. For example, if you’re setting up Jira for a marketing team, you might create a project called “Marketing Campaigns” and use it to track all ongoing and upcoming campaigns.
2. Define Task Types
In Jira, tasks are known as issues. You can create different issue types to represent different kinds of tasks. For example, a marketing team might have issue types like “Blog Post,” “Social Media Update,” or “Email Campaign.” An HR team might create issue types like “Job Posting,” “Onboarding,” or “Employee Review.”
By defining different issue types, you ensure that each task has its own category, making it easier to track and manage them within the project.
3. Set Up Task Boards
Once your project is set up, you’ll have access to a task board where you can organize tasks visually. You can customize the columns to reflect your workflow stages. For task management, common columns include “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done,” but you can add additional stages if needed.
For example, a marketing team might add columns like “Awaiting Approval” or “Ready for Launch,” while an HR team might include stages like “Interview Scheduled” or “Offer Sent.”
4. Assign Tasks and Set Deadlines
After creating tasks, you can assign them to team members, set deadlines, and add details like attachments or comments. Jira allows you to prioritize tasks, making sure the most urgent work is completed first. You can also set dependencies between tasks, ensuring that one task is completed before another starts.
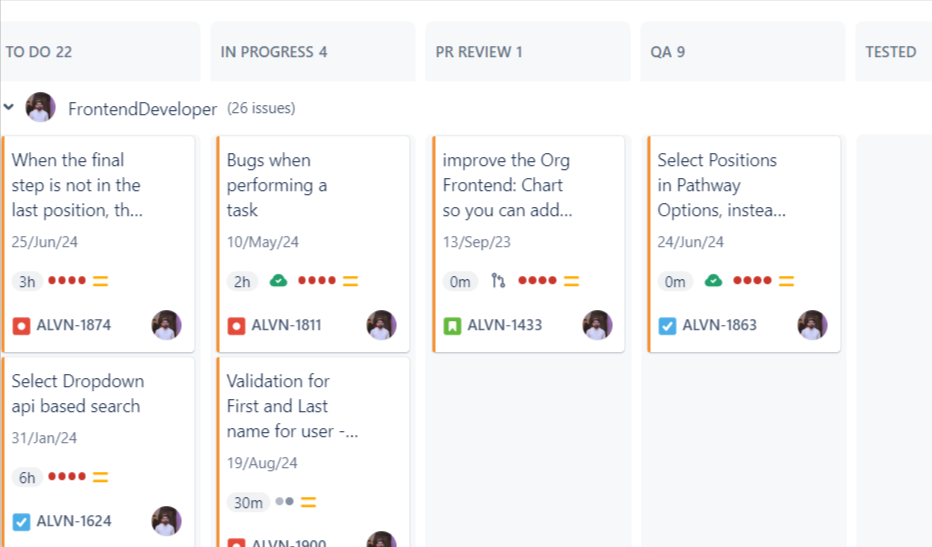
For example, in a marketing team, the task for writing a blog post might depend on completing the task for topic approval. These dependencies help keep the team on track and avoid bottlenecks.
5. Use Jira Reports to Track Progress
Jira comes with a range of reporting options that are highly beneficial for task management. You can generate reports that show how many tasks have been completed, which tasks are overdue, and how efficiently your team is working. Reports like the Burndown Chart or Cumulative Flow Diagram can give insights into team performance and help identify areas for improvement.
By regularly reviewing these reports, team leaders can adjust workloads, reassign tasks, or address any blockers that are slowing down progress.
Pros of Using Jira for Task Management
There are several reasons why Jira is a strong contender for managing tasks across various teams and industries.
1. Customization and Flexibility
Jira’s customization options allow teams to tailor their workflows, task boards, and issue types to fit their specific needs. Whether you’re managing a simple to-do list or complex workflows, Jira can be adapted to suit your requirements.
For example, a marketing team might have a completely different setup than an operations team, but both can use Jira effectively by customizing it to their needs.
2. Task Visibility and Transparency
Jira’s task boards provide a clear overview of all ongoing tasks, who is responsible for each one, and where they are in the workflow. This transparency ensures that everyone on the team knows what’s being worked on and what’s coming up next.
For teams that manage multiple tasks or projects simultaneously, this visibility is crucial to keeping everything on track.
3. Scalability
One of Jira’s key advantages is its scalability. Whether you’re a small startup managing a few tasks or a large enterprise handling complex projects, Jira can grow with your team. Its features are robust enough to manage tasks for any team size and project complexity.
4. Real-Time Collaboration
The ability to comment on tasks, upload files, and tag team members directly in Jira promotes collaboration and reduces the need for multiple communication channels. This real-time collaboration is especially valuable for remote teams or teams working across different time zones.
5. Integrations with Other Tools
Jira integrates seamlessly with other popular tools, such as Slack, Google Drive, and Confluence. This integration helps teams manage tasks and projects across multiple platforms while keeping everything centralized in Jira.
6. Reporting and Analytics
Jira includes powerful reporting tools that allow you to track task progress, monitor team performance, and identify bottlenecks. This helps managers make informed decisions and improve efficiency.
7. Agile Task Management
For teams that follow Agile methodologies, Jira is a natural fit. It includes features like sprint planning, backlogs, and burndown charts, which help Agile teams stay on track and manage their tasks efficiently.
How Jira Compares to Other Task Management Tools
How does Jira stack up against other popular task management tools? Here’s a comparison with three other popular platforms like Trello, Asana, and Monday.com.
1. Jira vs. Trello
Trello, also owned by Atlassian, is a simpler task management tool. It uses Kanban boards for managing tasks, much like Jira, but is more straightforward and easier to use. Trello is ideal for teams with simple task management needs and is much quicker to set up than Jira.
However, Trello lacks the advanced reporting and customization features that Jira offers. Teams looking for a more powerful tool to handle complex workflows may find Trello too limited.
2. Jira vs. Asana
Asana is another popular task management tool known for its clean, user-friendly interface. Like Jira, Asana offers customizable task boards, workflows, and reporting. However, Asana is generally easier to use and has a less steep learning curve.
While Asana is great for task management, it doesn’t offer the same level of flexibility and customization that Jira does. Teams looking for more control over their workflows might prefer Jira’s advanced features.
3. Jira vs. Monday.com
Monday.com is a highly visual task management tool that allows teams to manage tasks, projects, and workflows through customizable boards. Like Jira, Monday.com offers a high level of customization and is highly scalable.
However, Monday.com is generally seen as more user-friendly and quicker to set up than Jira. Teams looking for a balance between customization and ease of use might prefer Monday.com, especially if they don’t need Jira’s advanced features.
Best Practices for Using Jira for Task Management
Jira is a versatile and powerful tool, but its full potential can only be realized when used strategically. Below are several best practices that can help teams maximize their productivity and efficiency when using Jira for task management.
1. Customize Workflows to Fit Your Team’s Processes
Jira’s ability to customize workflows is one of its standout features. Each team has different processes, and with Jira, you can create workflows that reflect the stages tasks go through within your organization.
By tailoring workflows to fit your team’s processes, you reduce confusion and streamline task movement through different stages.
Review and update your workflows regularly to adapt to any changes in your team’s processes. As your team evolves, so should your workflows.
2. Use Labels and Filters to Organize Tasks
Jira’s labeling and filtering features allow for better organization, especially when managing large volumes of tasks. This feature allows you to search for tasks based on criteria such as assignee, status, labels, due dates, or project. Filters can be saved and shared with other team members. They can also be applied to dashboards, giving you a quick overview of the team’s progress at a glance.
Labels help categorize tasks into relevant groups, while filters help you quickly locate specific tasks based on various criteria. Encourage team members to apply relevant labels consistently. This will make it easier to search for tasks and create filtered views.
Once in a while, review and refine your labeling system to ensure it still meets the needs of the team. Too many labels can cause confusion, so keep things simple and relevant.
3. Take Advantage of Jira’s Automation Features
One of Jira’s hidden gems is its automation capabilities, which can save your team a lot of manual effort. Automation rules can be set up to trigger specific actions based on predefined conditions. This reduces repetitive tasks, minimizes human error, and increases efficiency.
Select from pre-built automation rules or create your own custom rules based on triggers and actions that suit your workflow. Automations can be configured for individual projects or applied globally across all projects in Jira.
Start small with automation to ensure it works as expected, then gradually increase the complexity of your automation rules. Review automation logs to monitor their effectiveness and adjust rules as needed.
4. Break Down Large Tasks into Sub-Tasks
Large tasks can often be overwhelming, which can lead to delays or confusion. Jira allows you to break down these larger tasks into smaller, more manageable sub-tasks. This is particularly useful for teams managing complex projects with multiple steps or contributors.
Use sub-tasks to promote accountability within the team. Having smaller, clearly defined tasks makes it easier to monitor progress and ensures that no one feels overwhelmed by the complexity of larger tasks.
5. Implement Agile Methodologies (if Applicable)
Jira is designed with Agile methodologies in mind, so if your team uses Agile practices like Scrum or Kanban, make sure to fully use Jira’s features for Agile task management.
Using Jira for Scrum:
- Set up a Scrum board to organize tasks into sprints, with clear start and end dates.
- Use backlog grooming sessions to prioritize upcoming tasks and move them into sprints.
- Hold sprint reviews and retrospectives to evaluate what worked well and what could be improved for the next sprint.
Using Jira for Kanban:
- For continuous workflows, Kanban boards provide a visual representation of work in progress.
- Use Work in Progress (WIP) limits to prevent the team from taking on too many tasks at once, ensuring that work flows smoothly through the board.
Jira also offers Agile-specific reports, such as velocity charts and sprint burndown reports, to help Agile teams monitor their progress.
6. Train Your Team on Jira’s Features
To get the most out of Jira for task management, it’s essential to ensure that all team members are properly trained on how to use the tool. Jira has many features, and without adequate training, some of these may be underused.
Provide a thorough onboarding for new team members, including a basic walkthrough of Jira’s main features, such as creating tasks, using labels, and navigating boards.
Create an internal knowledge base or guide specific to your team’s use of Jira. This can include step-by-step instructions for common tasks, workflows, and best practices. Encourage team members to explore Jira’s help documentation and support resources if they encounter challenges.
By following these best practices, your team can use Jira not only as a task management tool but also as a way to improve collaboration, productivity, and accountability. The key is to take full advantage of Jira’s customization, automation, and reporting features, while continuously refining your processes to match your team’s unique needs, ensuring smoother workflows and more efficient task management over time.
Final Thoughts: Is Jira the Right Task Management Tool for You?
Jira is a powerful tool that can be adapted for task management in various industries and teams. Its flexibility, scalability, and advanced features make it a great choice for teams managing complex workflows or large numbers of tasks.
If your team is already using Jira for software development or project management, it’s a natural fit to extend its use to task management.
In the end, the decision comes down to your team’s needs. If you need a highly customizable tool that can handle complex tasks and workflows, Jira is a great option.
As an Atlassian partner, we can help you maximize your Jira experience, whether you’re looking to integrate it for task management or optimize your existing setup. Reach out to us for expert advice, and implementation services, or to explore how Jira can be tailored to meet your team’s unique requirements.
Introduction
Jira is a project management tool used by teams worldwide to track issues, manage tasks, and organize workflows. One of its most powerful features is the customizable dashboard, which serves as a central hub for tracking all relevant project information. However, many users only scratch the surface of what their Jira dashboard can do.
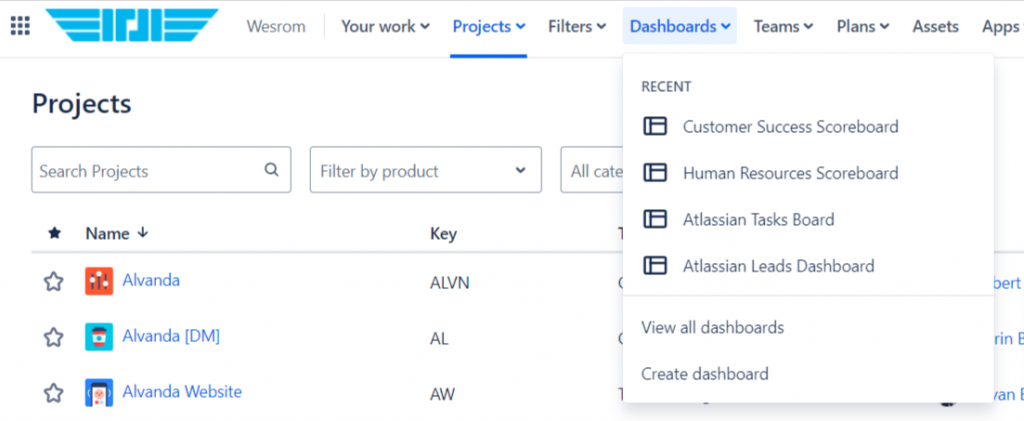
Customizing your Jira dashboard is more than just adding gadgets. It’s about tailoring it to match your team’s workflow, improving decision-making, and enhancing productivity. Whether you’re a project manager or a developer, an optimized dashboard gives you the insights you need without wasting time. This article will walk you through advanced techniques for customizing your Jira dashboard to suit your team’s specific needs.
Why Customizing Your Jira Dashboard Matters
Jira dashboards come with default settings, but these often don’t capture all the details a team needs to work efficiently. A customized dashboard gives your team a personalized space where they can focus on the data and metrics that matter most.
For example, a development team focused on sprints might need sprint health reports, while a customer support team might track open and resolved tickets. Without customization, teams waste time searching through cluttered or irrelevant data. A customized dashboard cuts through the noise and puts critical information front and center.
A well-designed dashboard reduces bottlenecks by keeping everyone informed, aligned, and focused on their priorities.
Getting Started with Jira Dashboard Customization
Before diving into the advanced tips, it’s important to get the basics right. Here’s a quick refresher on how to create and customize your Jira dashboard.
- Creating a Dashboard: Start by going to the “Dashboards” section in Jira and selecting “Create Dashboard.” From here, you can give your dashboard a name and description. You’ll also be able to choose whether the dashboard is private or shared with other team members.
- Adding Gadgets: Gadgets are the building blocks of your dashboard. You can add them by clicking on the “Add Gadget” button. Some popular gadgets include:
- Sprint Health: For tracking the status of your current sprint.
- Pie Chart: To visualize data like issues by status or assignee.
- Filter Results: Displays issues based on specific filters.
- Adjusting the Layout: Jira lets you drag and drop gadgets, so you can arrange them based on importance. Place high-priority gadgets near the top and group related ones together. This makes your dashboard easier to navigate and use.
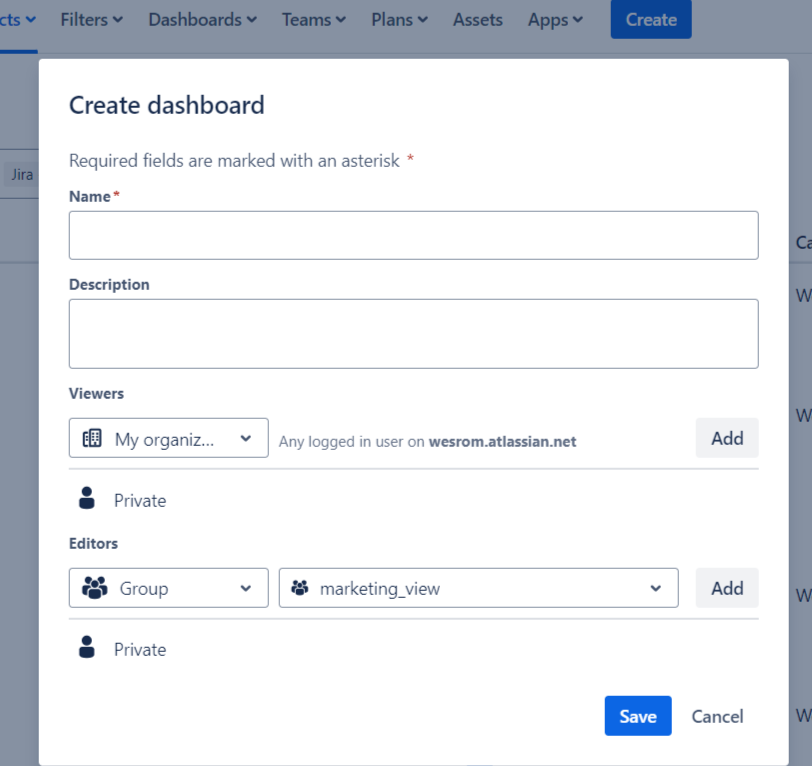
Once you’ve set up the basics, it’s time to look at more advanced customizations.
Advanced Tips for Customizing Jira Dashboards
Optimizing Layout for Agile or Kanban Teams
Agile and Kanban teams have different ways of working, and your dashboard layout should reflect that. Agile teams often work in sprints, so it’s helpful to display sprint-related data like burndown charts, sprint health, and the number of issues completed versus remaining. Kanban teams, on the other hand, focus on continuous work. They may benefit from gadgets that track ongoing tasks, like the Control Chart or Cumulative Flow Diagram.
Practical Example:
- Agile Team: You might arrange your dashboard with a Sprint Health gadget at the top, followed by a Sprint Burndown chart, and an Issue Statistics gadget showing the number of tasks completed.
- Kanban Team: Your layout could start with the Cumulative Flow Diagram, followed by a Control Chart to monitor cycle times, and a Filter Results gadget showing tasks that are blocked.
Tailoring the layout to your team’s workflow keeps key metrics in view and helps the team stay focused.
Mastering Jira Gadgets
Gadgets are the heart of your Jira dashboard, and there’s a lot more to them than just the basics. Some advanced gadgets you might want to explore include:
- Two-Dimensional Filter Statistics: This gadget lets you view data across two dimensions, such as assignee versus status or project versus issue type. It’s especially useful for large teams managing multiple projects.
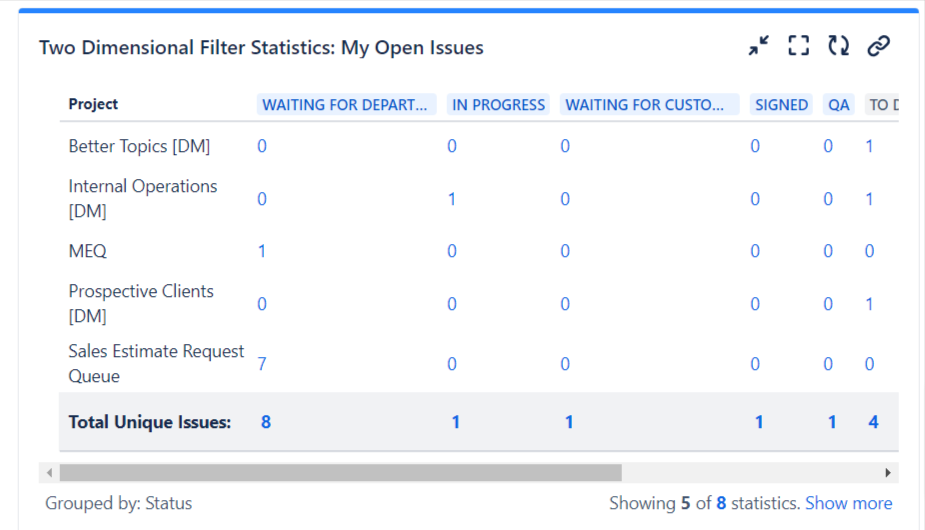
- Agile Sprint Health: This gadget provides a detailed view of sprint progress, including the number of tasks completed, in progress, and blocked.
- Created vs. Resolved Issues: This gadget shows the balance between issues created and resolved over a certain period, helping you manage your backlog.
For each gadget, you can apply custom filters that limit the data displayed. For example, if you only want to see high-priority issues, you can apply a filter to display only those.
Implementing Jira Automation
Jira Automation can save your team a lot of time by automatically updating your dashboard when certain conditions are met. For instance, you can set an automation rule to update the dashboard when a sprint is completed or when a task is moved to “Done.”
Practical Automation Examples:
- Auto-refresh gadgets: Set rules to update your Sprint Health gadget or burndown chart every time a sprint ends or begins.
- Automating issue tracking: You can set automation rules to automatically assign tasks or send notifications when an issue is moved to a certain status (like “In Review” or “Blocked”).
By leveraging automation, your dashboard will always display the most current information without manual updates.
Custom Filters for Personalized Data Insights
Custom filters allow you to tailor your dashboard to show exactly what you need. Jira Query Language (JQL) is a powerful tool for building these filters. Some examples of useful custom filters include:
- High-priority issues: Use a JQL query like
priority = Highto track only critical tasks. - Tasks due soon: Create a filter for issues with due dates in the next week using a query like
due <= 7d. - Assigned to a specific team member: Track tasks assigned to a particular person by using
assignee = [username].
You can combine these filters with gadgets for even more precise tracking. For example, pair a Filter Results gadget with a custom filter for tasks due within the next two weeks to keep deadlines front and center.
Enhancing Collaboration with Shared Dashboards
Shared dashboards allow team members to work from the same set of data, improving collaboration. For example, a project manager may need a high-level view of the project’s progress, while a developer may need to focus on specific tasks assigned to them.
When creating shared dashboards, remember to set user permissions carefully. Some data, such as sprint reports, may be useful to the entire team, while more detailed issue tracking might be reserved for developers.
Using Third-Party Integrations
Jira’s flexibility is one of its greatest strengths, and third-party integrations can further enhance your dashboard’s functionality. Popular integrations include:
- Tempo Timesheets: This tool helps teams track time spent on each task, making it easier to manage resources and meet deadlines.
- eazyBI: If you need advanced reporting, eazyBI offers customizable charts and reports that you can embed directly into your dashboard.
- Slack Integration: You can set up notifications in Slack that link directly to your Jira dashboard, making it easier to stay updated on task progress without switching between apps.
Best Practices for Maintaining and Updating Jira Dashboards
Customizing your Jira dashboard isn’t a one-time task; it requires regular updates and tweaks to ensure it continues to meet your team’s needs. As projects progress, new priorities and tasks emerge, meaning that the tools and data points your team focuses on will also change. Following best practices ensures your dashboard stays functional, organized, and useful for all team members.
Regular Dashboard Reviews
It’s crucial to schedule regular reviews of your Jira dashboard to make sure it reflects the current status of your project. For example, if your team has shifted focus from development to bug fixing, the dashboard should highlight bugs and their priority levels. Regularly revisiting your dashboard setup also helps prevent data overload and ensures that the gadgets and filters are still relevant. Set a monthly or bi-weekly review process where team members can suggest changes or provide feedback about the dashboard’s effectiveness.
Updating Filters and Gadgets
As projects evolve, some filters and gadgets might become irrelevant or outdated. Gadgets tracking sprint progress may need to be reset or adjusted with each new sprint, while custom filters pulling data from older projects should be updated to include only the current workload. Ensure that filters are always tuned to display the most pertinent data.
Keeping Dashboards Simple and Focused
It’s easy to fall into the trap of adding too many gadgets to your dashboard, especially when trying to cater to the needs of multiple users. However, an overly cluttered dashboard makes it difficult to focus on critical tasks. Choose only the most important metrics to display and avoid duplicating data. Less is often more when it comes to dashboard efficiency.
Regularly Monitoring Performance
Dashboards loaded with complex gadgets or extensive filters can sometimes slow down performance, particularly if they pull in data from multiple projects or large datasets. Keep an eye on load times and dashboard responsiveness. If performance slows, review which gadgets are causing the delays and consider simplifying the queries or using lighter gadgets.
Custom Dashboards for Different Teams
One dashboard doesn’t have to serve everyone’s needs. Consider creating separate dashboards tailored to different roles within your team. For instance, a project manager might benefit from a high-level overview, while developers need more granular information about specific tasks and issues.
By following these practices, your Jira dashboard can evolve alongside your projects, ensuring it remains an integral tool for your team’s workflow without becoming outdated or overloaded.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Dashboard Customization
Customizing your Jira dashboard is not without its challenges. While the goal is to create a more effective workspace, certain common mistakes can hinder your dashboard’s efficiency or make it less useful for your team. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for, along with solutions to avoid them.
Overloading the Dashboard with Gadgets
One of the most frequent mistakes teams make is adding too many gadgets. A dashboard crammed with gadgets can overwhelm users and obscure the important data they need to act on. Too much information can slow decision-making as users struggle to find the right metric in a sea of data.
Keep your dashboard simple by only displaying key metrics that are directly relevant to the user’s role. For example, a team lead might only need high-level data like sprint health, while a developer may benefit from seeing their task backlog and active issues. Regularly audit the dashboard to remove gadgets that aren’t essential.
Using Outdated or Unnecessary Filters
Filters are a powerful tool for narrowing down data, but using old filters that no longer apply to the current project will result in outdated information cluttering your dashboard. This makes the dashboard less useful and can even lead to confusion if users are viewing irrelevant tasks or old project data.
Regularly review and update your custom filters. For example, if a project is completed, update your filters to focus on new projects and sprints. Always ensure that gadgets are pulling live data by setting accurate date ranges and keeping JQL queries up to date.
Neglecting User Permissions
Jira allows for varying levels of user permissions across dashboards. A common error occurs when permissions are not carefully managed, leading to sensitive information being visible to the wrong team members, or conversely, relevant team members being unable to access the dashboard at all.
Ensure that your dashboard’s permissions are set correctly. For instance, shared dashboards should be accessible only to those who need to view them, and private dashboards should only include data relevant to the dashboard owner.
Lack of Clear Organization
Another common mistake is neglecting to organize the dashboard logically. A disorganized layout can make it difficult for users to interpret the data, especially when gadgets are scattered without purpose or priority.
Arrange your dashboard in a way that flows naturally. Place the most important gadgets (e.g., Sprint Health, Burndown Chart) at the top, and less critical gadgets (e.g., Task Completion Status) lower down. Group related gadgets together to make it easy for users to find what they’re looking for without having to scroll excessively.
Failing to Adapt the Dashboard Over Time
A dashboard that worked for your team during the initial phases of a project may not be as effective once the project advances. Failing to adapt the dashboard to reflect new objectives, team structures, or workflows can make it less useful and potentially lead to decreased productivity.
As your project moves forward, be sure to adapt your dashboard to new goals or workflows. If your team shifts focus from development to bug fixing, for instance, make sure your gadgets and filters reflect that shift. Update automation rules and gadgets regularly to ensure the data displayed aligns with current team priorities.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your Jira dashboard remains a powerful tool that boosts your team’s productivity, provides clear insights, and supports efficient workflows.
Final Thoughts
As Atlassian partners, we understand the full potential of Jira and how customized dashboards can transform the way your teams work. By implementing the advanced techniques outlined in this guide, your team can gain deeper insights, improve efficiency, and stay focused on the tasks that matter most. Whether you’re managing a small team or coordinating multiple projects across departments, a well-structured Jira dashboard can be a game-changer for your productivity.
If your company is ready to take its project management to the next level with Jira, or if you’re looking for expert advice on how to fully leverage Jira’s capabilities, we’re here to help. Contact us today to explore how we can optimize Jira for your unique needs and drive success for your teams.
Introduction
Delivering high-quality code quickly is a top priority in software development. To stay competitive, teams must streamline their workflows to ensure that code is tested, integrated, and deployed efficiently. Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices play a crucial role in achieving this goal. However, implementing CI/CD can be challenging without the right tools. This is where Bitbucket Pipelines comes in.

Bitbucket Pipelines is an integrated CI/CD service that automates the process of building, testing, and deploying code directly from your Bitbucket repository. This article will guide you through setting up and optimizing Bitbucket Pipelines to streamline your development workflow. Whether you’re new to CI/CD or looking to enhance your current setup, this guide will provide the insights you need to get the most out of Bitbucket Pipelines.
What is Bitbucket Pipelines?
Bitbucket Pipelines is a cloud-based CI/CD service offered by Atlassian as part of their Bitbucket platform. It allows you to automate various stages of your software development process, such as code compilation, testing, and deployment, all from within your Bitbucket repository.
Key features of Bitbucket Pipelines include:
- Cloud-Native Environment: No need to set up or maintain servers—everything runs in the cloud.
- YAML-Based Configuration: Pipelines are defined using simple YAML files, making it easy to customize and manage your workflows.
- Seamless Integration: Bitbucket Pipelines integrates smoothly with other Atlassian tools like Jira and Confluence, as well as third-party services like AWS, Docker, and Kubernetes.
Compared to other CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Travis CI, Bitbucket Pipelines stands out for its deep integration with Bitbucket and its ease of use. Jenkins, for example, offers more flexibility and customization but requires more setup and maintenance. Bitbucket Pipelines, on the other hand, is ideal for teams that want a straightforward, no-fuss CI/CD solution that works out of the box.
Setting Up Bitbucket Pipelines
Setting up Bitbucket Pipelines is a straightforward process, especially if you already have a Bitbucket repository. Below is a step-by-step guide to getting your first pipeline up and running.
Prerequisites
Before setting up Bitbucket Pipelines, ensure that you have:
- A Bitbucket account
- A repository in Bitbucket where your project code is hosted
Step-by-Step Setup
- Enable Pipelines in Your Repository:
- Navigate to your Bitbucket repository.
- Click on the “Pipelines” tab in the left-hand menu.
- Follow the prompts to enable Pipelines for your repository.
- Create a YAML Configuration File:
- In the root directory of your repository, create a file named
bitbucket-pipelines.yml. This file will define your pipeline configuration. Here’s a simple example – this configuration tells Bitbucket Pipelines to run two commands:npm installto install project dependencies andnpm testto run tests:
- In the root directory of your repository, create a file named
pipelines:
default:
- step:
name: Build and Test
script:
- npm install
- npm test
- Run Your First Pipeline:
- Once you’ve committed the
bitbucket-pipelines.ymlfile to your repository, Bitbucket Pipelines will automatically trigger the pipeline. You can monitor the progress of your pipeline in the Pipelines tab.
- Once you’ve committed the
- Visualizing the Process:
- To help users follow along, consider including screenshots of each step. Visual aids can make the setup process clearer, especially for users who are new to Bitbucket Pipelines.
By following these steps, you’ll have a basic pipeline running in no time. However, this is just the beginning. Next, we’ll explore how to optimize your pipeline for better performance and efficiency.
Optimizing Your Development Workflow with Bitbucket Pipelines
Once you’ve set up Bitbucket Pipelines, there are several ways to optimize it for your specific needs. These optimizations can help you save time, reduce errors, and ensure that your pipeline runs as efficiently as possible.
Automating Builds and Deployments
Automation is one of the key benefits of CI/CD. With Bitbucket Pipelines, you can automate the entire process of building, testing, and deploying your code. For example, you can configure your pipeline to automatically deploy code to a staging environment after a successful build and test. This ensures that your code is always in a deployable state and reduces the risk of human error.
Example YAML Configuration for Automated Deployment:
pipelines:
branches:
master:
- step:
name: Build and Test
script:
- npm install
- npm test
- step:
name: Deploy to Staging
script:
- npm run deploy-staging
In this example, the pipeline runs tests first, and if successful, it proceeds to deploy the code to a staging environment.
Using Environment Variables
Environment variables allow you to manage configurations for different environments, such as development, staging, and production. This makes your pipeline more flexible and secure since sensitive information (like API keys) can be stored as environment variables rather than hardcoded in your scripts.
To set environment variables:
- Go to your Bitbucket repository settings.
- Click on “Pipelines” and then “Environment variables.”
- Add your variables, which will be accessible within your pipeline scripts.
Using environment variables, you can configure your pipeline to deploy to different environments based on the branch or tag being built.
Managing Multiple Pipelines
For more complex projects, you may need multiple pipelines to handle different workflows. Bitbucket Pipelines supports the use of multiple pipelines within the same repository. For example, you can create separate pipelines for testing, deployment, and release management.
Example YAML Configuration for Multiple Pipelines:
pipelines:
branches:
feature/*:
- step:
name: Feature Branch Testing
script:
- npm install
- npm test
master:
- step:
name: Production Deployment
script:
- npm install
- npm test
- npm run deploy-production
This configuration runs different pipelines depending on the branch pattern. Feature branches undergo testing, while the master branch is used for production deployment.
Optimizing Pipeline Performance
To get the most out of Bitbucket Pipelines, you should look at ways to optimize performance. One effective method is to use parallel steps, which allow you to run multiple tasks simultaneously. This can significantly reduce the time it takes for your pipeline to complete.
Example of Parallel Steps:
pipelines:
default:
- parallel:
- step:
name: Run Unit Tests
script:
- npm run test-unit
- step:
name: Run Integration Tests
script:
- npm run test-integration
In this example, unit tests and integration tests are run in parallel, reducing overall build time.
Another optimization technique is to use caching. By caching dependencies or build artifacts, you can avoid re-downloading or rebuilding them in every pipeline run, which speeds up subsequent runs.
Example of Caching:
pipelines:
default:
- step:
caches:
- node
script:
- npm install
- npm test
In this configuration, the node_modules directory is cached, so it doesn’t need to be reinstalled in every run.
Integrating with Docker
Docker is widely used in modern development for containerizing applications. Bitbucket Pipelines integrates well with Docker, allowing you to build, test, and deploy Docker images as part of your CI/CD process.
Example YAML Configuration with Docker:
image: docker:latest
pipelines:
default:
- step:
script:
- docker build -t my-app .
- docker run my-app npm test
In this example, a Docker image is built and then used to run tests. This approach is particularly useful for microservices architectures where each service might have its own Docker image.
Best Practices for YAML Configuration
Here are some tips for writing effective YAML configurations:
- Keep It Simple: Avoid complex scripts. Break down tasks into clear, manageable steps.
- Use Comments: Comment your YAML files to explain what each section does. This makes it easier for others to understand and maintain the pipeline.
- Test Locally: Test your pipeline configuration locally before pushing changes to catch errors early.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your pipeline is easy to manage and maintain, even as your project grows.
Advanced Bitbucket Pipelines Features
As you become more familiar with Bitbucket Pipelines, you can start exploring some of its advanced features. These features allow you to customize your CI/CD process further and integrate it with other tools and services.
Integrating with Jira
If your team uses Jira for issue tracking and project management, you can integrate it with Bitbucket Pipelines to create a seamless workflow. For example, you can configure your pipeline to automatically update Jira issues based on the status of your builds and deployments.
Example Integration:
- Linking Jira Issues: You can link commits and branches in Bitbucket to specific Jira issues by including the issue key (e.g., “JIRA-123”) in your commit messages. This automatically updates the Jira issue with the commit details and build status.
- Deployment Tracking: Jira can automatically track deployments from Bitbucket Pipelines, allowing you to see which issues are deployed to which environments.
Using Bitbucket Pipelines with Cloud Providers
Bitbucket Pipelines can be used to deploy applications to various cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. By configuring deployment scripts in your YAML file, you can automate the process of deploying your application to the cloud, ensuring consistent and reliable deployments.
Example YAML Configuration for AWS Deployment:
pipelines:
default:
- step:
script:
- pipe: atlassian/aws-s3-deploy:0.3.1
variables:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: $AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: $AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
S3_BUCKET: 'my-bucket-name'
LOCAL_PATH: 'build/'
ACL: 'public-read'
This example shows how to deploy a build directory to an S3 bucket on AWS. Similar configurations can be used for other cloud providers.
Pipeline Triggers and Conditions
Bitbucket Pipelines allows you to set up custom triggers and conditions for running pipelines. This means you can configure your pipelines to run only under specific circumstances, such as when a pull request is created or when a tag is pushed.
Example of Conditional Triggers:
pipelines:
pull-requests:
'**':
- step:
name: Run Tests on Pull Requests
script:
- npm install
- npm test
tags:
'v*.*.*':
- step:
name: Deploy on Version Tags
script:
- npm run deploy-production
In this example, tests are run on all pull requests, and deployments are triggered only when a version tag is pushed.
Real-World Use Cases
To better understand the impact of Bitbucket Pipelines, let’s explore some real-world use cases. These examples will illustrate how different companies have used Bitbucket Pipelines to improve their development workflows.
Use Case 1: Small Development Team
A small development team working on a web application needed a simple CI/CD solution that didn’t require a lot of setup or maintenance. They chose Bitbucket Pipelines because of its integration with Bitbucket and its ease of use.

By setting up a basic pipeline with automated tests and deployments to their staging environment, the team was able to significantly reduce the time spent on manual testing and deployment. This allowed them to focus more on coding and less on managing their development workflow.
Use Case 2: Large Enterprise with Multiple Teams
A large enterprise with multiple development teams was struggling with inconsistent CI/CD practices across different projects. They decided to standardize on Bitbucket Pipelines to ensure a consistent approach to CI/CD.
Each team was able to define their own pipelines within a standardized framework, allowing them to tailor their pipelines to their specific needs while maintaining consistency across the organization. The enterprise also integrated Bitbucket Pipelines with Jira to automatically track the status of issues and deployments.
Use Case 3: Start-up Scaling Rapidly
A start-up that was scaling rapidly needed a CI/CD solution that could grow with them. They started with a simple pipeline in Bitbucket Pipelines but quickly expanded it to include multiple stages, parallel steps, and integration with AWS for automated deployments.
As the start-up grew, they added more advanced features like conditional triggers and pipeline caching, allowing them to keep their CI/CD process efficient and scalable.
Best Practices for Using Bitbucket Pipelines
To get the most out of Bitbucket Pipelines, it’s important to follow best practices. These guidelines will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure that your pipeline remains efficient and maintainable as your project grows.
Modularity in Pipelines
Breaking down your pipeline into modular steps can make it easier to manage and maintain. For example, you can separate testing, building, and deployment into different steps, allowing you to reuse them across different branches or projects.
Keeping Pipelines Simple and Readable
A pipeline should be easy to understand at a glance. Avoid overly complex scripts or configurations, and use comments to explain the purpose of each step. This makes it easier for team members to contribute and troubleshoot when necessary.
Regularly Review and Update Pipelines
As your project evolves, your pipeline should too. Regularly review your pipeline configurations to ensure they are still meeting your needs. Update scripts and dependencies as necessary, and take advantage of new features in Bitbucket Pipelines as they become available.
Using Caching and Parallel Steps
Leverage caching and parallel steps to optimize the performance of your pipeline. Caching can reduce build times by reusing dependencies, while parallel steps allow you to run tasks simultaneously, reducing the overall time it takes for your pipeline to complete.
Monitor and Optimize Pipeline Performance
Regularly monitor the performance of your pipelines. Bitbucket provides insights into pipeline performance, allowing you to identify bottlenecks and optimize your configurations. Look for steps that take longer than expected and consider ways to optimize them, such as by using faster executors or simplifying the tasks.
Final Thougths
Bitbucket Pipelines offers a powerful yet user-friendly solution for automating your CI/CD workflows. As an Atlassian partner, we have a deep understanding of how Bitbucket Pipelines can transform your development workflow. Whether you’re a small team looking to streamline your processes or a large enterprise seeking to standardize CI/CD practices across multiple projects, Bitbucket Pipelines offers the flexibility and power you need.
By leveraging our expertise, we can help you integrate Bitbucket Pipelines seamlessly into your existing workflow, ensuring that you get the most out of this powerful tool. Our team is here to guide you every step of the way, from initial setup to ongoing optimization, making sure that your CI/CD process is as efficient and reliable as possible.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you integrate Bitbucket Pipelines into your development workflow and take your software delivery to the next level.