Introduction
Jira is a project management tool used by teams worldwide to track issues, manage tasks, and organize workflows. One of its most powerful features is the customizable dashboard, which serves as a central hub for tracking all relevant project information. However, many users only scratch the surface of what their Jira dashboard can do.
Customizing your Jira dashboard is more than just adding gadgets. It’s about tailoring it to match your team’s workflow, improving decision-making, and enhancing productivity. Whether you’re a project manager or a developer, an optimized dashboard gives you the insights you need without wasting time. This article will walk you through advanced techniques for customizing your Jira dashboard to suit your team’s specific needs.
Why Customizing Your Jira Dashboard Matters
Jira dashboards come with default settings, but these often don’t capture all the details a team needs to work efficiently. A customized dashboard gives your team a personalized space where they can focus on the data and metrics that matter most.
For example, a development team focused on sprints might need sprint health reports, while a customer support team might track open and resolved tickets. Without customization, teams waste time searching through cluttered or irrelevant data. A customized dashboard cuts through the noise and puts critical information front and center.
A well-designed dashboard reduces bottlenecks by keeping everyone informed, aligned, and focused on their priorities.
Getting Started with Jira Dashboard Customization
Before diving into the advanced tips, it’s important to get the basics right. Here’s a quick refresher on how to create and customize your Jira dashboard.
- Creating a Dashboard: Start by going to the “Dashboards” section in Jira and selecting “Create Dashboard.” From here, you can give your dashboard a name and description. You’ll also be able to choose whether the dashboard is private or shared with other team members.
- Adding Gadgets: Gadgets are the building blocks of your dashboard. You can add them by clicking on the “Add Gadget” button. Some popular gadgets include:
- Sprint Health: For tracking the status of your current sprint.
- Pie Chart: To visualize data like issues by status or assignee.
- Filter Results: Displays issues based on specific filters.
- Adjusting the Layout: Jira lets you drag and drop gadgets, so you can arrange them based on importance. Place high-priority gadgets near the top and group related ones together. This makes your dashboard easier to navigate and use.
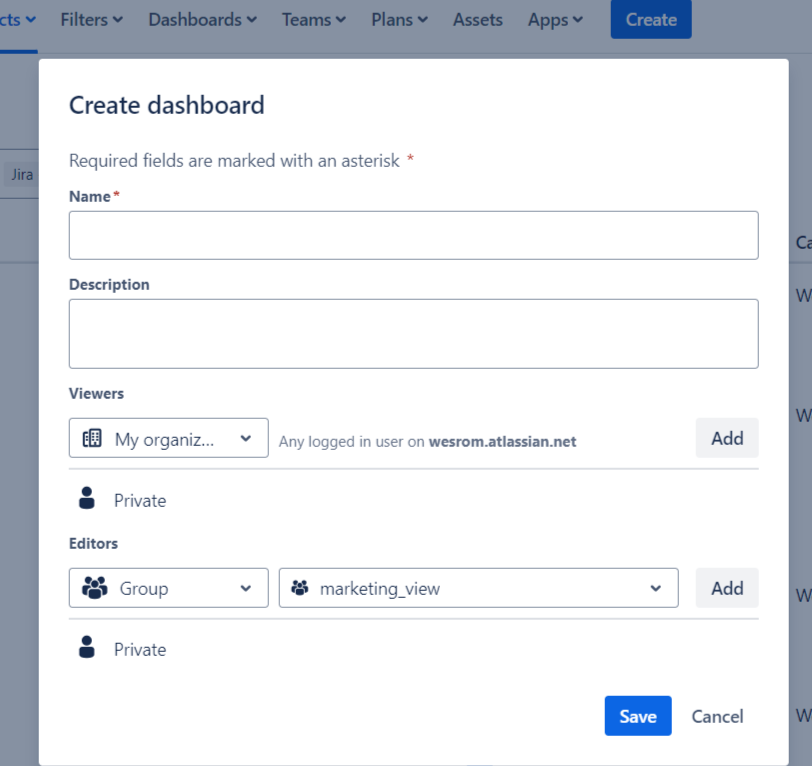
Once you’ve set up the basics, it’s time to look at more advanced customizations.
Advanced Tips for Customizing Jira Dashboards
Optimizing Layout for Agile or Kanban Teams
Agile and Kanban teams have different ways of working, and your dashboard layout should reflect that. Agile teams often work in sprints, so it’s helpful to display sprint-related data like burndown charts, sprint health, and the number of issues completed versus remaining. Kanban teams, on the other hand, focus on continuous work. They may benefit from gadgets that track ongoing tasks, like the Control Chart or Cumulative Flow Diagram.
Practical Example:
- Agile Team: You might arrange your dashboard with a Sprint Health gadget at the top, followed by a Sprint Burndown chart, and an Issue Statistics gadget showing the number of tasks completed.
- Kanban Team: Your layout could start with the Cumulative Flow Diagram, followed by a Control Chart to monitor cycle times, and a Filter Results gadget showing tasks that are blocked.
Tailoring the layout to your team’s workflow keeps key metrics in view and helps the team stay focused.
Mastering Jira Gadgets
Gadgets are the heart of your Jira dashboard, and there’s a lot more to them than just the basics. Some advanced gadgets you might want to explore include:
- Two-Dimensional Filter Statistics: This gadget lets you view data across two dimensions, such as assignee versus status or project versus issue type. It’s especially useful for large teams managing multiple projects.
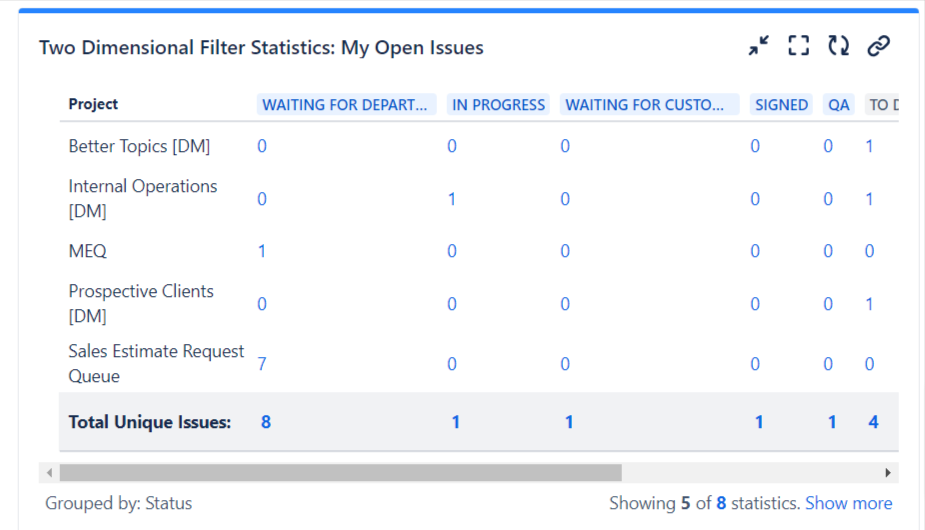
- Agile Sprint Health: This gadget provides a detailed view of sprint progress, including the number of tasks completed, in progress, and blocked.
- Created vs. Resolved Issues: This gadget shows the balance between issues created and resolved over a certain period, helping you manage your backlog.
For each gadget, you can apply custom filters that limit the data displayed. For example, if you only want to see high-priority issues, you can apply a filter to display only those.
Implementing Jira Automation
Jira Automation can save your team a lot of time by automatically updating your dashboard when certain conditions are met. For instance, you can set an automation rule to update the dashboard when a sprint is completed or when a task is moved to “Done.”
Practical Automation Examples:
- Auto-refresh gadgets: Set rules to update your Sprint Health gadget or burndown chart every time a sprint ends or begins.
- Automating issue tracking: You can set automation rules to automatically assign tasks or send notifications when an issue is moved to a certain status (like “In Review” or “Blocked”).
By leveraging automation, your dashboard will always display the most current information without manual updates.
Custom Filters for Personalized Data Insights
Custom filters allow you to tailor your dashboard to show exactly what you need. Jira Query Language (JQL) is a powerful tool for building these filters. Some examples of useful custom filters include:
- High-priority issues: Use a JQL query like
priority = Highto track only critical tasks. - Tasks due soon: Create a filter for issues with due dates in the next week using a query like
due <= 7d. - Assigned to a specific team member: Track tasks assigned to a particular person by using
assignee = [username].
You can combine these filters with gadgets for even more precise tracking. For example, pair a Filter Results gadget with a custom filter for tasks due within the next two weeks to keep deadlines front and center.
Enhancing Collaboration with Shared Dashboards
Shared dashboards allow team members to work from the same set of data, improving collaboration. For example, a project manager may need a high-level view of the project’s progress, while a developer may need to focus on specific tasks assigned to them.
When creating shared dashboards, remember to set user permissions carefully. Some data, such as sprint reports, may be useful to the entire team, while more detailed issue tracking might be reserved for developers.
Using Third-Party Integrations
Jira’s flexibility is one of its greatest strengths, and third-party integrations can further enhance your dashboard’s functionality. Popular integrations include:
- Tempo Timesheets: This tool helps teams track time spent on each task, making it easier to manage resources and meet deadlines.
- eazyBI: If you need advanced reporting, eazyBI offers customizable charts and reports that you can embed directly into your dashboard.
- Slack Integration: You can set up notifications in Slack that link directly to your Jira dashboard, making it easier to stay updated on task progress without switching between apps.
Best Practices for Maintaining and Updating Jira Dashboards
Customizing your Jira dashboard isn’t a one-time task; it requires regular updates and tweaks to ensure it continues to meet your team’s needs. As projects progress, new priorities and tasks emerge, meaning that the tools and data points your team focuses on will also change. Following best practices ensures your dashboard stays functional, organized, and useful for all team members.
Regular Dashboard Reviews
It’s crucial to schedule regular reviews of your Jira dashboard to make sure it reflects the current status of your project. For example, if your team has shifted focus from development to bug fixing, the dashboard should highlight bugs and their priority levels. Regularly revisiting your dashboard setup also helps prevent data overload and ensures that the gadgets and filters are still relevant. Set a monthly or bi-weekly review process where team members can suggest changes or provide feedback about the dashboard’s effectiveness.
Updating Filters and Gadgets
As projects evolve, some filters and gadgets might become irrelevant or outdated. Gadgets tracking sprint progress may need to be reset or adjusted with each new sprint, while custom filters pulling data from older projects should be updated to include only the current workload. Ensure that filters are always tuned to display the most pertinent data.
Keeping Dashboards Simple and Focused
It’s easy to fall into the trap of adding too many gadgets to your dashboard, especially when trying to cater to the needs of multiple users. However, an overly cluttered dashboard makes it difficult to focus on critical tasks. Choose only the most important metrics to display and avoid duplicating data. Less is often more when it comes to dashboard efficiency.
Regularly Monitoring Performance
Dashboards loaded with complex gadgets or extensive filters can sometimes slow down performance, particularly if they pull in data from multiple projects or large datasets. Keep an eye on load times and dashboard responsiveness. If performance slows, review which gadgets are causing the delays and consider simplifying the queries or using lighter gadgets.
Custom Dashboards for Different Teams
One dashboard doesn’t have to serve everyone’s needs. Consider creating separate dashboards tailored to different roles within your team. For instance, a project manager might benefit from a high-level overview, while developers need more granular information about specific tasks and issues.
By following these practices, your Jira dashboard can evolve alongside your projects, ensuring it remains an integral tool for your team’s workflow without becoming outdated or overloaded.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Dashboard Customization
Customizing your Jira dashboard is not without its challenges. While the goal is to create a more effective workspace, certain common mistakes can hinder your dashboard’s efficiency or make it less useful for your team. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for, along with solutions to avoid them.
Overloading the Dashboard with Gadgets
One of the most frequent mistakes teams make is adding too many gadgets. A dashboard crammed with gadgets can overwhelm users and obscure the important data they need to act on. Too much information can slow decision-making as users struggle to find the right metric in a sea of data.
Keep your dashboard simple by only displaying key metrics that are directly relevant to the user’s role. For example, a team lead might only need high-level data like sprint health, while a developer may benefit from seeing their task backlog and active issues. Regularly audit the dashboard to remove gadgets that aren’t essential.
Using Outdated or Unnecessary Filters
Filters are a powerful tool for narrowing down data, but using old filters that no longer apply to the current project will result in outdated information cluttering your dashboard. This makes the dashboard less useful and can even lead to confusion if users are viewing irrelevant tasks or old project data.
Regularly review and update your custom filters. For example, if a project is completed, update your filters to focus on new projects and sprints. Always ensure that gadgets are pulling live data by setting accurate date ranges and keeping JQL queries up to date.
Neglecting User Permissions
Jira allows for varying levels of user permissions across dashboards. A common error occurs when permissions are not carefully managed, leading to sensitive information being visible to the wrong team members, or conversely, relevant team members being unable to access the dashboard at all.
Ensure that your dashboard’s permissions are set correctly. For instance, shared dashboards should be accessible only to those who need to view them, and private dashboards should only include data relevant to the dashboard owner.
Lack of Clear Organization
Another common mistake is neglecting to organize the dashboard logically. A disorganized layout can make it difficult for users to interpret the data, especially when gadgets are scattered without purpose or priority.
Arrange your dashboard in a way that flows naturally. Place the most important gadgets (e.g., Sprint Health, Burndown Chart) at the top, and less critical gadgets (e.g., Task Completion Status) lower down. Group related gadgets together to make it easy for users to find what they’re looking for without having to scroll excessively.
Failing to Adapt the Dashboard Over Time
A dashboard that worked for your team during the initial phases of a project may not be as effective once the project advances. Failing to adapt the dashboard to reflect new objectives, team structures, or workflows can make it less useful and potentially lead to decreased productivity.
As your project moves forward, be sure to adapt your dashboard to new goals or workflows. If your team shifts focus from development to bug fixing, for instance, make sure your gadgets and filters reflect that shift. Update automation rules and gadgets regularly to ensure the data displayed aligns with current team priorities.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your Jira dashboard remains a powerful tool that boosts your team’s productivity, provides clear insights, and supports efficient workflows.
Final Thoughts
As Atlassian partners, we understand the full potential of Jira and how customized dashboards can transform the way your teams work. By implementing the advanced techniques outlined in this guide, your team can gain deeper insights, improve efficiency, and stay focused on the tasks that matter most. Whether you’re managing a small team or coordinating multiple projects across departments, a well-structured Jira dashboard can be a game-changer for your productivity.
If your company is ready to take its project management to the next level with Jira, or if you’re looking for expert advice on how to fully leverage Jira’s capabilities, we’re here to help. Contact us today to explore how we can optimize Jira for your unique needs and drive success for your teams.
We all know that nowadays efficiency and productivity are crucial for success. Teams are constantly looking for tools and methods to streamline their workflows, improve collaboration, and manage projects more effectively.

Jira and Confluence, two powerful tools by Atlassian, have become popular choices for project management and documentation. Individually, they offer robust features, but when integrated, they provide a seamless workflow that can significantly enhance productivity. This article will explore how integrating Jira and Confluence can streamline project management, enhance collaboration, and help teams work more efficiently.
Understanding Jira and Confluence
What is Jira?
Jira is a project management tool designed to help teams plan, track, and manage their work. Originally created for bug and issue tracking, Jira has evolved to support various types of project management, including agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban. Key features of Jira include customizable workflows, issue tracking, sprint planning, and reporting capabilities. These features make Jira an ideal choice for software development teams, but its flexibility also makes it suitable for a wide range of industries.
What is Confluence?
Confluence is a collaborative workspace where teams can create, share, and store documents. It serves as a central hub for team collaboration, knowledge sharing, and documentation. Confluence allows users to create pages and spaces for different projects, organize content with templates, and use powerful search functions to find information quickly. Whether it’s creating project documentation, meeting notes, or a knowledge base, Confluence helps teams keep their information organized and accessible.
Why Are These Tools Popular?
Jira and Confluence are popular because they address the core needs of modern teams: efficient project management and effective collaboration. By providing a structured way to manage tasks and projects, Jira helps teams stay organized and focused. Confluence, on the other hand, offers a user-friendly platform for creating and sharing content, making it easy for teams to collaborate and stay informed. Together, these tools create a powerful ecosystem that supports all aspects of teamwork.
The Benefits of Integrating Jira and Confluence
Seamless Project Management and Documentation
Integrating Jira and Confluence allows teams to link project tasks with related documentation easily. For example, when working on a project, developers can use Jira to track coding tasks and link them to detailed technical documentation stored in Confluence. This integration helps ensure that all relevant information is readily accessible, reducing the time spent searching for documents and improving efficiency. Team members can quickly find everything they need in one place, leading to a more streamlined workflow.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
Effective communication is key to successful teamwork. When Jira and Confluence are integrated, team members can easily share updates, comments, and feedback. For instance, a team member can create a Confluence page to outline project requirements and link it to related Jira tasks. Other team members can comment directly on the Confluence page or the Jira issues, providing feedback and updates in real time. This integration ensures that everyone is on the same page, leading to better collaboration and fewer misunderstandings.
Enhanced Visibility and Transparency
One of the main benefits of integrating Jira and Confluence is the increased visibility it provides into project progress and status. Managers can use Jira to track the progress of tasks and issues and see how they align with the overall project plan stored in Confluence. This transparency helps teams identify potential bottlenecks early and make informed decisions. With clear visibility into project status, teams can stay on track and meet their deadlines more effectively.
Centralized Information and Easy Access
By integrating Jira and Confluence, teams can centralize all project-related information in one place. This centralization makes it easy for team members to access the information they need, whether it’s a task list in Jira or a project plan in Confluence. For example, a team member can quickly access a Confluence page from a Jira issue or view related Jira tasks from a Confluence page. This seamless access to information reduces the time spent searching for documents and ensures that everyone has the latest updates.
Reduced Duplication of Work
Integrating Jira and Confluence helps prevent duplication of work by linking related tasks and documents. For example, a project plan in Confluence can be linked to related tasks in Jira, ensuring that everyone is working from the same source of truth. This alignment helps reduce errors and ensures that work is completed efficiently. Team members can easily see which tasks are already being worked on and avoid duplicating efforts.

How to Integrate Jira and Confluence
Setting Permissions and User Roles
It’s important to manage permissions to ensure that team members have the right access to Jira and Confluence. Set up roles and permissions to control who can view, edit, and comment on tasks and documents. For example, developers might have edit access to Jira tasks but only view access to certain Confluence pages. Proper permissions help maintain data security and ensure that only authorized users can make changes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Integration
- Connecting Jira to Confluence:
- To integrate Jira and Confluence, you first need to ensure that both tools are set up and that you have administrative access. Go to the admin settings in Confluence and look for the Jira integration option. Follow the prompts to connect your Jira instance to Confluence. You will need the Jira URL and may need to generate an API token for authentication.
- Once the connection is established, you can start linking Jira issues to Confluence pages. For example, you can link a Jira task to a Confluence page by pasting the Jira issue URL into the page. This link creates a direct connection between the task and the related documentation.
- Using Confluence Macros for Jira:
- Confluence offers several macros that make it easy to display Jira information on Confluence pages. For example, you can use the “Jira Issues” macro to show a list of Jira tasks directly in a Confluence document. This feature helps team members see project progress without switching between tools.
- To use the Jira Issues macro, create a new Confluence page or edit an existing one. Click on the “Insert more content” button (usually represented by a “+” sign), select “Jira Issue/Filter,” and then configure the macro to display the relevant Jira issues. You can filter issues by project, issue type, assignee, or other criteria.
- Synchronizing Information Between the Two Platforms:
- Once Jira and Confluence are connected, you can start linking tasks and documents. For instance, you can link a Confluence page to a Jira issue by simply pasting the Jira issue URL into the page. This integration ensures that all related information is connected, making it easy to keep track of project details.
- Synchronization between Jira and Confluence can be further enhanced using automation rules. For example, you can set up rules in Jira to automatically create Confluence pages for new epics or tasks. This automation ensures that all necessary documentation is created and linked, saving time and ensuring consistency.
Use Cases for Jira and Confluence Integration
Software Development Project Management
Software development teams can benefit greatly from integrating Jira and Confluence. Developers can use Jira to track coding tasks, bugs, and issues, while Confluence can be used to store technical documentation, API references, and meeting notes. For example, a developer working on a new feature can use Jira to track the coding task and link it to a Confluence page with detailed specifications and design documents. This integration ensures that all project information is easily accessible, improving development efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.

Product Roadmap and Backlog Management
Product managers can use Confluence to create and share product roadmaps and backlogs. By linking these documents to Jira, teams can track the progress of features and tasks. For example, a product manager can create a Confluence page outlining the product roadmap, with links to related Jira epics and tasks. This integration helps teams stay aligned with the product vision and ensures that everyone is aware of the project’s priorities. It also allows product managers to update the roadmap and backlog in real-time, providing clear visibility into the project’s status.
Knowledge Base and Documentation
Teams can use Confluence to create a knowledge base with articles, how-tos, and FAQs. By linking these documents to related Jira tasks or issues, support teams can quickly find the information they need to resolve customer queries. For example, a support agent can use a Confluence page to document a common issue and link it to a Jira issue for tracking purposes. This setup improves customer support and reduces response times, as agents can easily access relevant information and track the status of reported issues.
Agile Sprint Planning and Tracking
Agile teams can use Jira for sprint planning and tracking, while Confluence can be used to document sprint goals, user stories, and retrospectives. For example, during sprint planning, the team can create a Confluence page outlining the sprint goals and user stories, with links to the corresponding Jira tasks. This integration helps teams plan effectively and review their progress at the end of each sprint, leading to continuous improvement. By having all sprint-related information in one place, teams can easily track their progress and make adjustments as needed.
Incident and Bug Tracking
When managing incidents and bugs, it is crucial to have detailed documentation. Confluence can be used to document incident reports and solutions, while Jira tracks the progress of resolving these issues. For example, when a bug is reported, a Jira issue can be created to track its resolution, with a linked Confluence page providing detailed information about the bug and the steps taken to resolve it. This integrated approach ensures that all information about the incident is documented and accessible, improving response times and reducing the impact of incidents.
Best Practices for Integrating Jira and Confluence
Consistent Naming Conventions
Use consistent naming conventions for projects, tasks, and documents to ensure clarity and easy navigation. For example, use the same project name in both Jira and Confluence, and use descriptive titles for tasks and documents. This consistency helps team members find what they need quickly and reduces confusion.
Regularly Update Links and Information
Ensure that links between Jira and Confluence are regularly updated to reflect the latest project status. For example, if a Jira task is completed, update the linked Confluence page to reflect this change. Keeping links and information up-to-date ensures that everyone has access to the latest information and reduces the risk of outdated or incorrect information.
Training and Onboarding
Provide training for team members on how to use Jira and Confluence effectively. This training should cover basic features, integration setup, and best practices. For example, offer training sessions or create a Confluence page with tutorials and FAQs to help team members get up to speed quickly. Proper training ensures that team members can use the tools effectively and make the most of the integration.
Automation and Customization
Take advantage of automation features to streamline workflows. For example, use Jira automation rules to automatically create Confluence pages for new tasks or epics. Customizing Jira and Confluence to fit your team’s specific needs can further improve efficiency and productivity. Consider creating custom templates for Confluence pages or using Jira plugins to extend functionality.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Regularly gather feedback from team members on the integration and look for ways to improve. For example, conduct surveys or hold feedback sessions to understand how the integration is working and identify areas for improvement. Continuous improvement ensures that the integration continues to meet the team’s needs and supports ongoing productivity gains.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Challenge: Complexity of Integration Setup
Setting up integration between Jira and Confluence can be complex, especially for teams with limited technical expertise. To overcome this challenge, provide clear documentation and step-by-step guides for the setup process. For example, create a Confluence page with detailed instructions on how to connect Jira and Confluence, including screenshots and troubleshooting tips. Offering training sessions or workshops can also help team members understand the integration process.
Challenge: Managing Permissions
Managing permissions can be challenging, especially in large organizations with many users. To address this challenge, clearly define roles and responsibilities for accessing Jira and Confluence. For example, set up user roles in Jira and Confluence and assign permissions based on these roles. Regularly review and update permissions to ensure that they align with the team’s needs.
Challenge: Keeping Information Up-to-Date
Keeping information up-to-date across both Jira and Confluence can be challenging, especially as projects evolve. To overcome this challenge, establish clear guidelines for updating information and ensure that team members follow them. For example, create a checklist for updating links and information when tasks are completed or new information is added. Use automation tools to help keep information synchronized between Jira and Confluence.
Challenge: User Adoption
Getting team members to adopt and use the integrated tools effectively can be a challenge. To address this, provide training and support to help team members understand the benefits of integration and how to use the tools effectively. For example, create a Confluence page with training materials, tutorials, and best practices for using Jira and Confluence. Encourage team members to use the tools regularly and provide ongoing support to address any questions or concerns.
Future Trends and Developments
Enhanced Integration Features
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see enhanced integration features between Jira and Confluence. These features may include more advanced automation capabilities, improved user interfaces, and better integration with other tools. For example, future developments may allow for even more seamless synchronization between Jira and Confluence, making it easier to keep information up-to-date and accessible.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are likely to play a growing role in project management and collaboration tools. For example, AI could be used to analyze project data and provide insights into team performance, identify potential risks, or suggest improvements. Machine learning could also be used to automate routine tasks, such as linking Jira issues to Confluence pages or creating project reports.
Greater Customization and Flexibility
Future developments may also focus on providing greater customization and flexibility for users. This could include more customizable templates, advanced reporting capabilities, and more options for integrating with other tools. For example, teams may be able to create custom workflows that better align with their specific processes and needs.
Conclusion
Integrating Jira and Confluence offers a powerful solution for enhancing productivity, improving collaboration, and streamlining project management. By connecting these two tools, teams can centralize their information, gain better visibility into project progress, and reduce duplication of work. Whether it’s managing software development projects, creating a knowledge base, or planning agile sprints, the integration of Jira and Confluence enables teams to work more efficiently and effectively.
As Atlassian partners, we have the expertise to help you fully leverage these tools for your organization’s specific needs. If you’re considering integrating Jira and Confluence, or looking to optimize your current setup, we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us today to learn how we can help your team achieve greater productivity and collaboration with a tailored integration solution.